Significant Parameters About Singapore Virtual Bank By Aspire
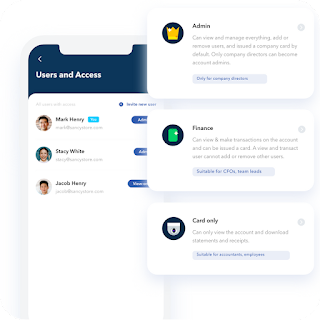
Singapore virtual bank is a financial institution that provides banking services via electronic means. These banks offer all of their services online and do not have any physical locations. Clients can use a smartphone app or the virtual bank's website to create an account, make deposits, take out loans, and execute other banking operations, saving time by avoiding the need to visit a physical bank. These banks should primarily participate in retail activities. To encourage financial inclusion, they should not impose any minimum account balance requirements or low-balance penalties on their clients.
Virtual banking is a new service. These banks, on the other hand, have been functioning in Europe, the United States, Japan, and other nations for some time. These banks have been shown to save money on rent and labour in other countries. When combined with fintech's innovation and increased efficiency, they can provide clients with competitive, personalised, and convenient banking services as well as an entirely new experience. Despite having no parentage in or links to the banking and financial services business, organisations are awarded licences to establish such banks. The licences provided by Singapore's banking authorities are a good example of this.
Virtual Bank Authorization
On 30 May 2018, the HKMA released a new Guideline on Authorization of Virtual Banks (Guideline) to help with the launch of virtual banks. The Guideline lays out the principles that the HKMA will consider when considering whether or not to approve virtual banks. The HKMA must be satisfied that the minimal requirements for permission in the Seventh Schedule to the Banking Ordinance (Ordinance) are met when deciding whether to grant or deny an application for authorization, as stated in the Guideline. The HKMA's "Guideline on Minimum Requirements for Authorization," published under section 16 (10) of the Ordinance, should be consulted for more information on how the HKMA would interpret these licencing criteria. Singapore virtual bank must comply with the same set of regulatory standards as traditional banks. The Regulatory & Supervisory Framework, Supervisory Policy Manual, Guidelines, and Circulars detail the supervisory methodology and regulatory obligations that apply to all banks. However, under a risk-based and technology-neutral approach, some regulatory criteria are modified to meet the business models of virtual banks. A virtual bank is one that primarily provides retail banking services over the internet or other electronic means rather than through physical locations.
Opportunity To Offer Customers More Innovative Products Open API Framework
The notion of open banking originates from the use of APIs to allow developers to create apps that allow financial data and information to be shared across multiple financial institutions, fintechs, and third-party providers with a customer's permission. Singapore virtual bank licences have been something of a work in progress over the past few years. As conventional banks and other competitors strive to deliver the most creative services to optimise customer experience, customers will be provided better, more efficient, more customer-centric financial and non-financial goods. Customers may now open business bank account online and make e-commerce payments straight from their bank account using the open banking API, for example, without having to submit any personal information. The Open API Framework is not required by the HKMA, and it remains to be seen how many conventional banks will participate in this project.

Comments
Post a Comment